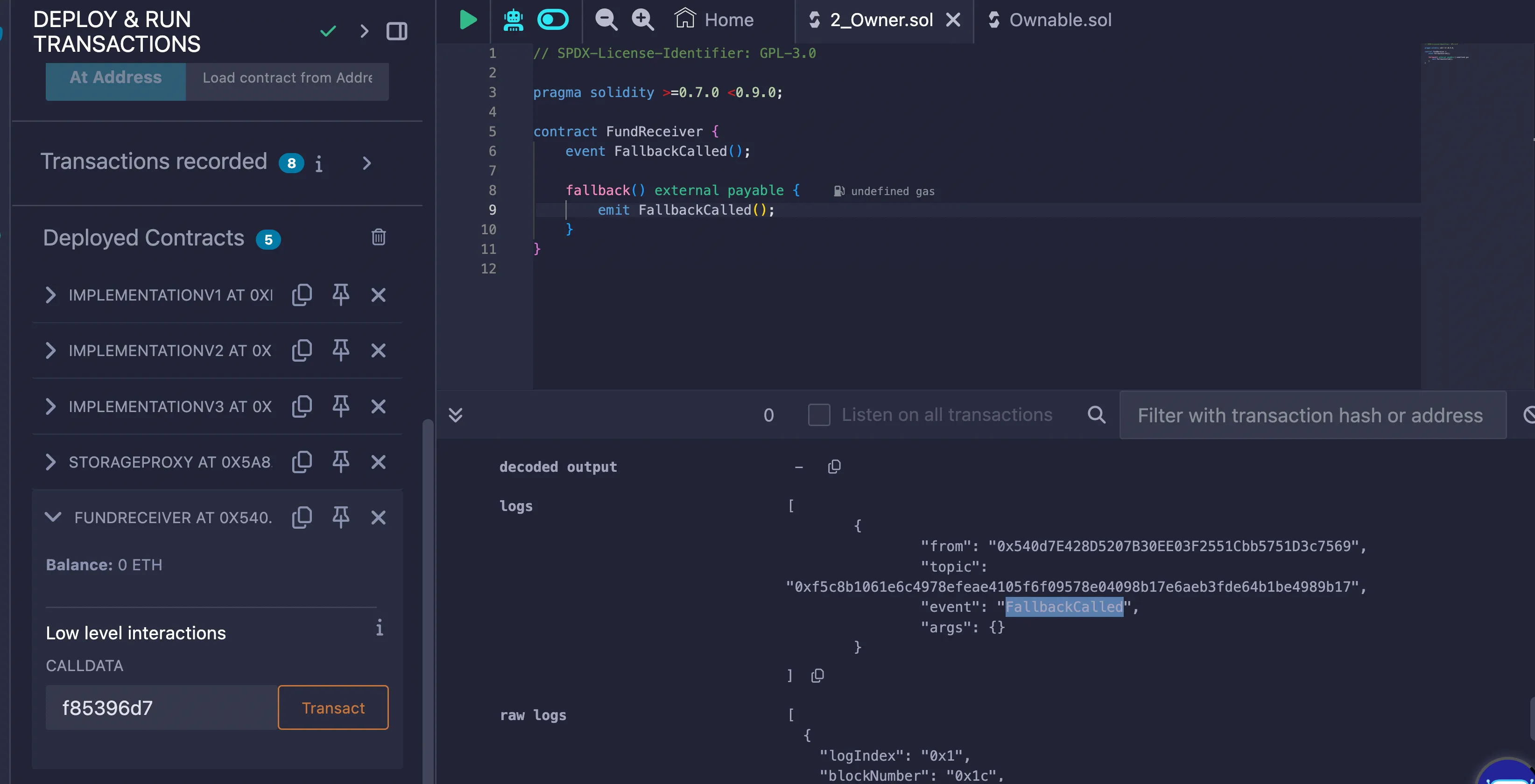
fallback Function
Ref - https://docs.soliditylang.org/en/v0.8.25/contracts.html#receive-ether-function
In Ethereum, the fallback function is a special function in a smart contract that is executed when the contract receives Ether and there is no other matching function signature for the call made. It is part of the low-level function set in Solidity and is commonly used for handling Ether transfers, handling unexpected function calls, or implementing custom logic for receiving Ether.
The fallback function is invoked when:
- The contract receives Ether via a plain transfer or call (i.e., no data is provided with the transaction or the data doesn’t match any existing function signature).
- The function call data does not match any function selector in the contract.
Properties of fallback fn
- It does not have a name (hence “fallback”).
- It cannot have any parameters.
- It cannot return anything (i.e., no return values).
- It is marked as
externaland payable if it needs to accept Ether. - It can be used to handle incoming Ether, execute arbitrary code, or forward calls to other contracts.
Code
// SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-3.0
pragma solidity >=0.7.0 <0.9.0;
contract FundReceiver { event FallbackCalled();
fallback() external payable { emit FallbackCalled(); }}