Asymetric Encryption
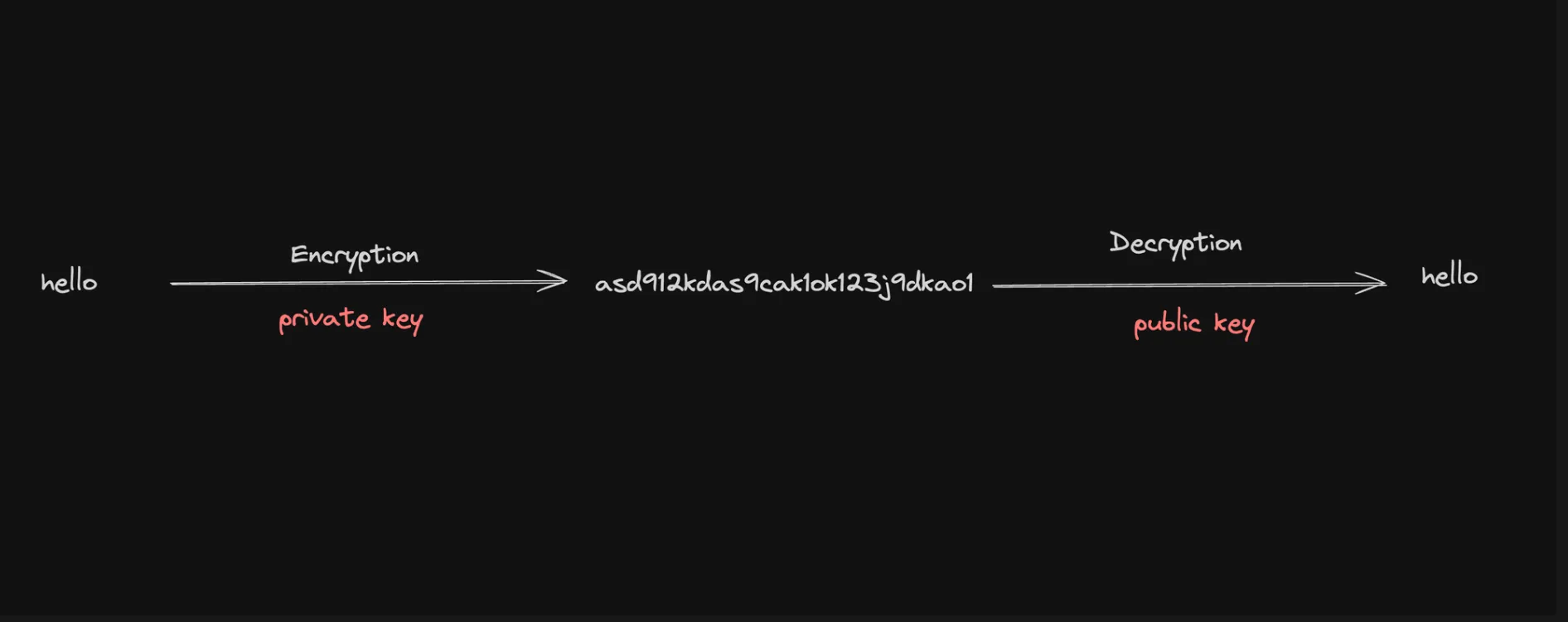
Asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key cryptography, is a type of encryption that uses a pair of keys: a public key and a private key. The keys are mathematically related, but it is computationally infeasible to derive the private key from the public key.
Public Key: The public key is a string that can be shared openly
Private Key: The private key is a secret cryptographic code that must be kept confidential. It is used to decrypt data encrypted with the corresponding public key or to create digital signatures.
Common Asymmetric Encryption Algorithms:
-
RSA - Rivest–Shamir–Adleman
-
ECC - Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECDSA) - ETH and BTC
-
EdDSA - Edwards-curve Digital Signature Algorithm - SOL

How eliptic curves work - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NF1pwjL9-DE&
Common eleptic curves
- secp256k1 - BTC and ETH
- ed25519 - SOL
Few usecases of public key cryptography -
- SSL/TLS certificates
- SSH keys to connect to servers/push to github
- Blockchains and cryptocurrencies