Wallets in ETH
Wallets are tools that allow users to store, manage, and interact with their cryptocurrencies. Here’s a breakdown of the key concepts:
Types of Wallets
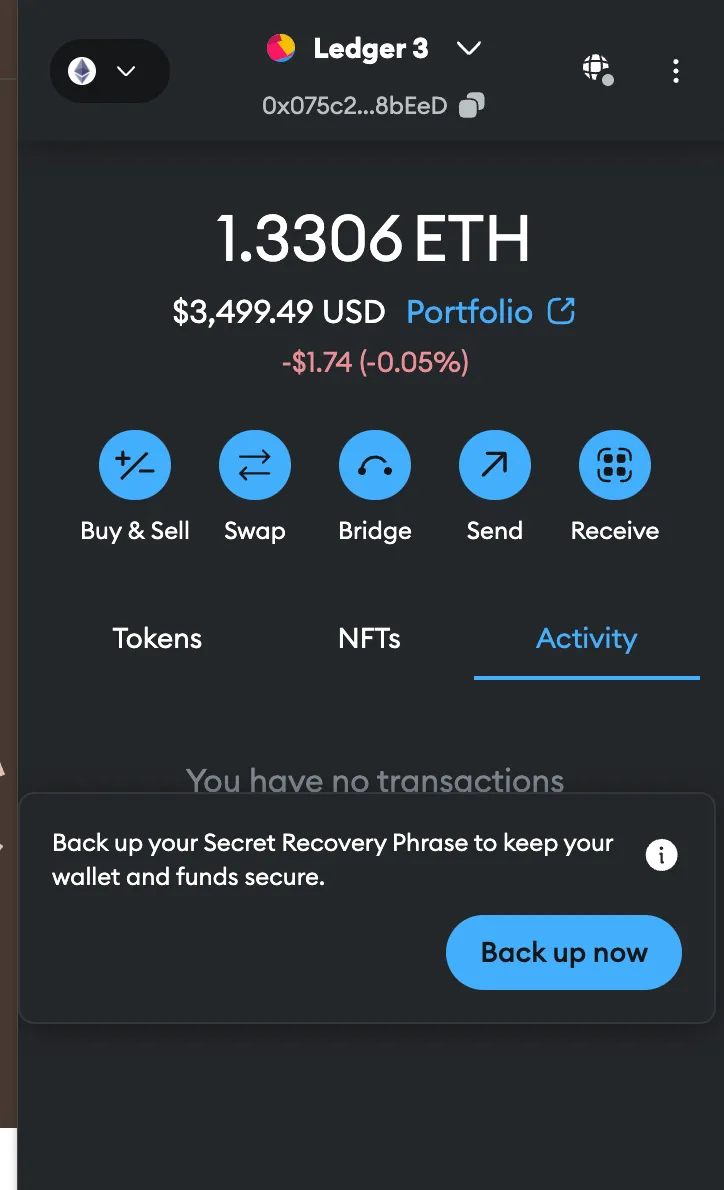
- Hot Wallets:
-
These are connected to the internet and are more convenient for frequent transactions. Examples include web wallets (like those on exchanges), mobile wallets, and desktop wallets.
-
- Cold Wallets:
-
These are offline wallets, making them more secure against hacks. Examples include hardware wallets (like Ledger or Trezor) and paper wallets.

-
Wallet Addresses
- A wallet address is a unique string of characters (usually starting with “0x” for Ethereum) that you can share with others to receive ETH or tokens. It’s similar to an account number.
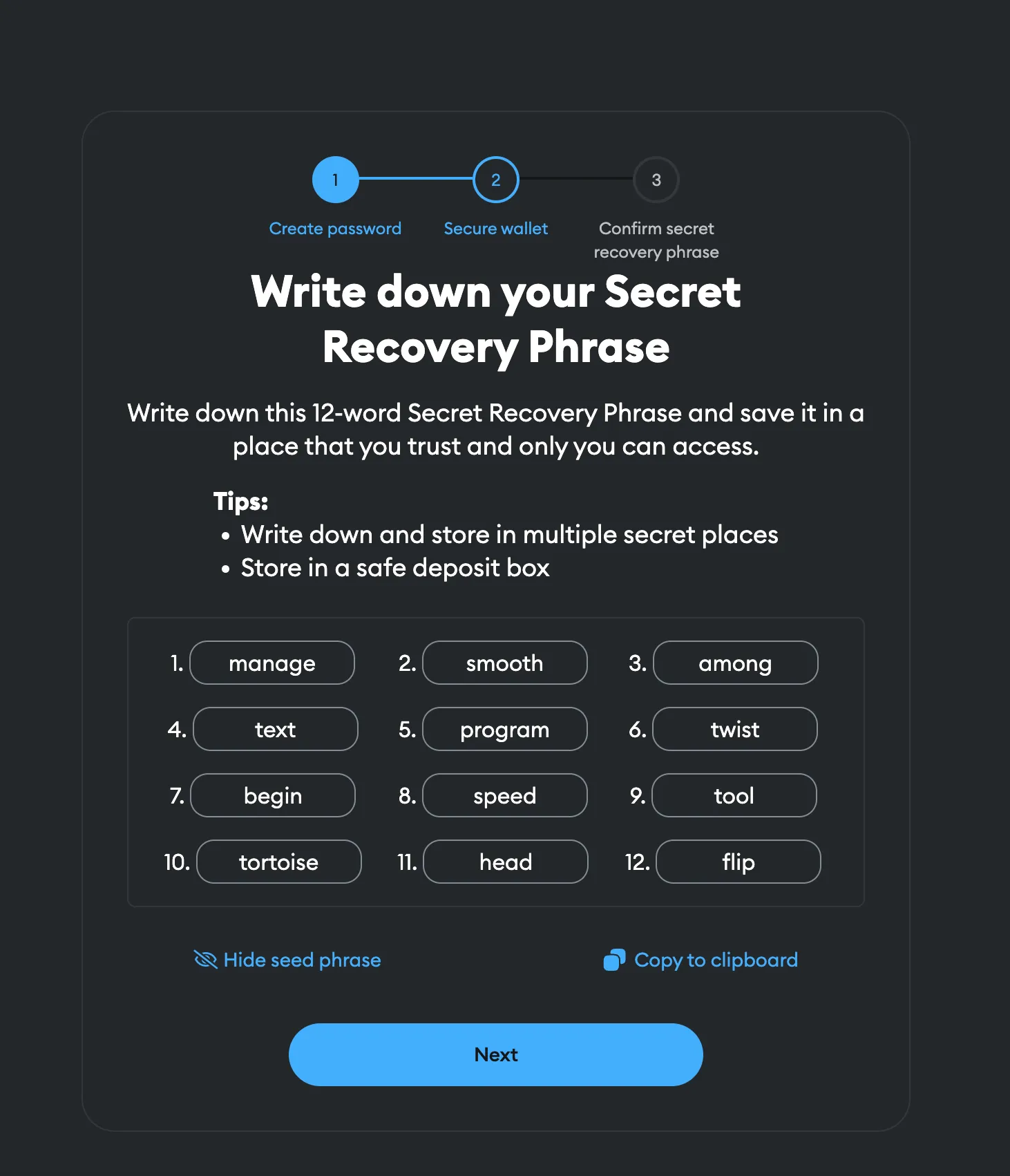
Seed Phrases
-
A seed phrase (or recovery phrase) is a series of words (typically 12 to 24) that acts as a master key for your wallet. It allows you to recover access to your wallet and its contents if you lose your device or forget your password. It’s crucial to keep this phrase secure and private, as anyone with access to it can control your funds.
Private Keys
- A private key is a secret number that allows you to access and manage your cryptocurrency. It’s mathematically linked to your wallet address, and anyone with access to your private key can control the funds in that wallet. Private keys should never be shared.